Fundation of Methodology (Session 4)
Session 4
Fundation of Methodology
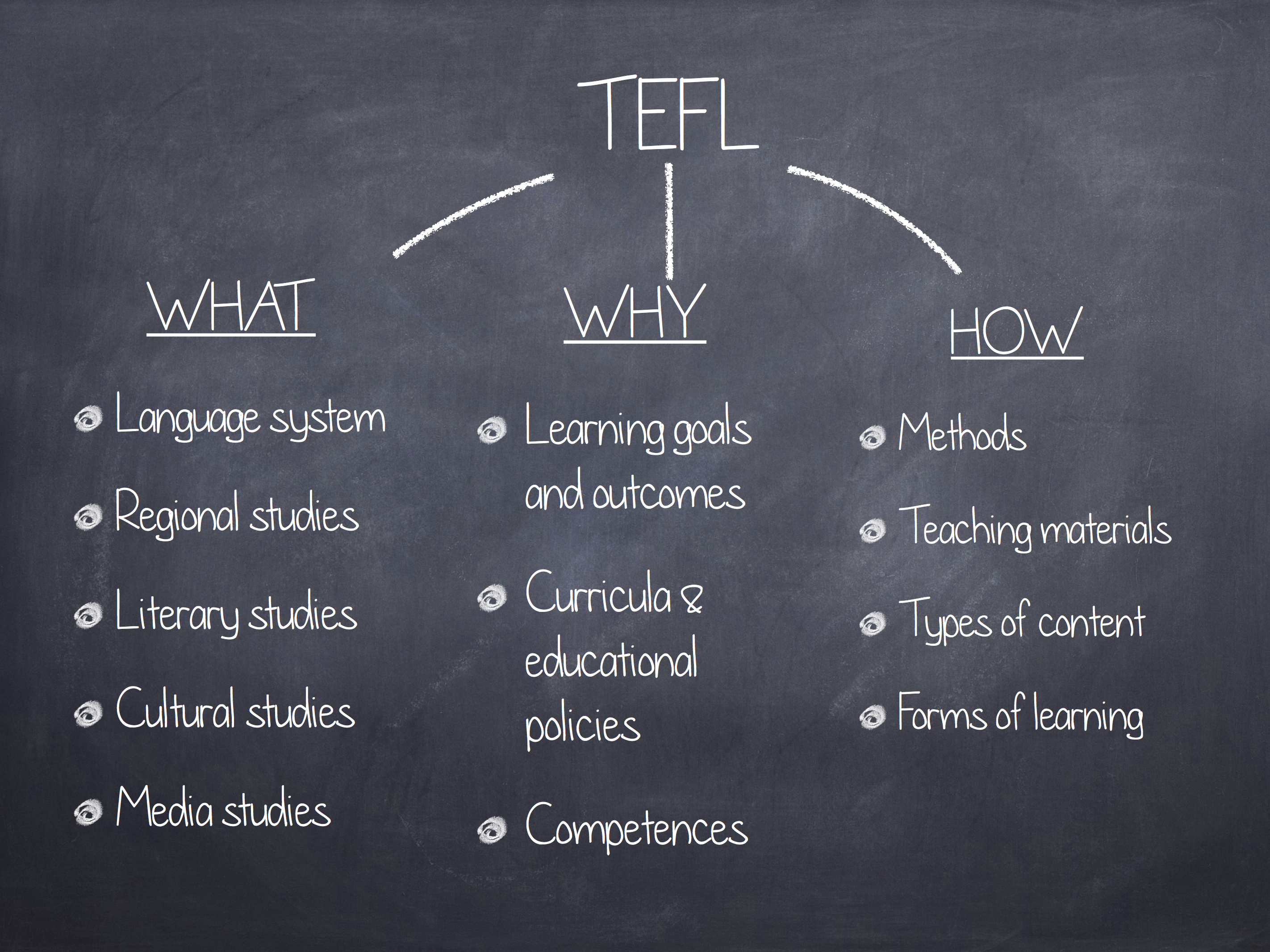
Trough the history teachers have asked for what is the right method for teaching a second language in order to get the competencies in the target language, Teachers need to know the meaning of the each concept regarding to methodology for putting them in practice by doing the curriculum and lesson plan as well, So it is necessary to give the meaning of Methodology, Approach, Method, and Techniques.
Mehodology
The study of pedagogical practices on general (including theoretical underpinnings and ralated reseach) Whatever considerations are involved in "how to teach" are methodological.
Approach
Theoretical positions and beliefs about the nature of language, the nature of language learning, and the applicability of both to pedagogical settings.
Method:
A generalized set of classroom specifications for accomplishing linguistic Objectives. Methods tend to be primarily concerned with teacher and students roles and behaviors and secondarily with such features as linguistic and subject-matter objectives, sequencing, and materials.
Curriculum/Syllabus:
Design for carrying out a particular language program. Features include a primary concern with the specification of linguistic and subject-matter objectives, sequencing, and materials to meet the needs of a designated group of learners in a defined context.
Technique:
Any of a wide variety of exercises, activities, or devices used in the language classroom for realizing lesson objectives
Approach
The audiolingual approach.
Behavioral psychology influenced audiolingualism. behaviourists believe that humans are organisms capable of learning many behaviour. It depends on three elements: Stimulus, Response, Reinforcement.
The cognitive approach: It holds that people do not learn complex systems like language or mathematics through habit formation but through the acquisition of patterns and rules that they can then extend and apply to new circumstances or problems.
Language learning is viewed as rule acquisition, not habit formation. Instruction is often individualized; learners are responsible for their own learning.
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario